 |
|
General Information about Canada
Location:Northern North America, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean and North Pacific Ocean, north of the conterminous US 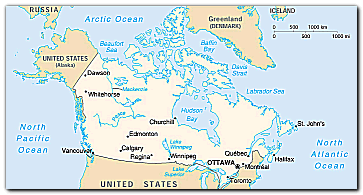
Geographic coordinates: 60 00 N, 95 00 W Map references: North America
Area:
Area—comparative: slightly larger than the US
Land boundaries:
Coastline: 243,791 km
Maritime claims:
Climate: varies from temperate in south to subarctic and arctic in north Terrain: mostly plains with mountains in west and lowlands in southeast
Elevation extremes:
Natural resources: nickel, zinc, copper, gold, lead, molybdenum, potash, silver, fish, timber, wildlife, coal, petroleum, natural gas
Land use:
Irrigated land: 7,100 sq km (1993 est.) Natural hazards: continuous permafrost in north is a serious obstacle to development; cyclonic storms form east of the Rocky Mountains, a result of the mixing of air masses from the Arctic, Pacific, and North American interior, and produce most of the country's rain and snow Environment—current issues: air pollution and resulting acid rain severely affecting lakes and damaging forests; metal smelting, coal-burning utilities, and vehicle emissions impacting on agricultural and forest productivity; ocean waters becoming contaminated due to agricultural, industrial, mining, and forestry activities
Environment—international agreements:
Geography—note: second-largest country in world (after Russia); strategic location between Russia and US via north polar route; nearly 90% of the population is concentrated within 160 km of the US/Canada border Population: 31,006,347 (July 1999 est.)
Age structure:
Population growth rate: 1.06% (1999 est.) Birth rate: 11.86 births/1,000 population (1999 est.) Death rate: 7.26 deaths/1,000 population (1999 est.) Net migration rate: 5.96 migrant(s)/1,000 population (1999 est.)
Sex ratio:
Infant mortality rate: 5.47 deaths/1,000 live births (1999 est.)
Life expectancy at birth:
Total fertility rate: 1.65 children born/woman (1999 est.)
Nationality:
Ethnic groups: British Isles origin 40%, French origin 27%, other European 20%, Amerindian 1.5%, other, mostly Asian 11.5% Religions: Roman Catholic 45%, United Church 12%, Anglican 8%, other 35% (1991) Languages: English (official), French (official)
Literacy:
Country name:
Data code: CA Government type: federation with parliamentary democracy Capital: Ottawa Administrative divisions: 10 provinces and 3 territories*; Alberta, British Columbia, Manitoba, New Brunswick, Newfoundland, Northwest Territories*, Nova Scotia, Nunavut*, Ontario, Prince Edward Island, Quebec, Saskatchewan, Yukon Territory* Independence: 1 July 1867 (from UK) National holiday: Canada Day, 1 July (1867) Constitution: 17 April 1982 (Constitution Act); originally, the machinery of the government was set up in the British North America Act of 1867; charter of rights and unwritten customs Legal system: based on English common law, except in Quebec, where civil law system based on French law prevails; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction, with reservations Suffrage: 18 years of age; universal
Executive branch:
Legislative branch:
bicameral Parliament or Parlement consists of the Senate or Senat (a body
whose members are appointed to serve until reaching 75 years of age by the
governor general and selected on the advice of the prime minister; its
normal limit is 104 senators) and the House of Commons or Chambre des
Communes (301 seats; members elected by direct popular vote to serve
five-year terms)
Judicial branch: Supreme Court, judges are appointed by the prime minister through the governor general Political parties and leaders: Liberal Party [Jean CHRETIEN]; Bloc Quebecois [Gilles DUCEPPE]; Reform Party [Preston MANNING]; New Democratic Party [Alexa MCDONOUGH]; Progressive Conservative Party [Joe CLARK] International organization participation: ACCT, AfDB, APEC, AsDB, Australia Group, BIS, C, CCC, CDB (non-regional), CE (observer), CP, EAPC, EBRD, ECE, ECLAC, ESA (cooperating state), FAO, G- 7, G-10, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICFTU, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Inmarsat, Intelsat, Interpol, IOC, IOM, ISO, ITU, MINURCA, MIPONUH, MTCR, NAM (guest), NATO, NEA, NSG, OAS, OECD, OPCW, OSCE, PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNDOF, UNESCO, UNFICYP, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIKOM, UNMIBH, UNMOP, UNPREDEP, UNTSO, UNU, UPU, WCL, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTrO, ZC
Diplomatic representation in the US:
Diplomatic representation from the US:
Economy—overview: As an affluent, high-tech industrial society, Canada today closely resembles the US in its market-oriented economic system, pattern of production, and high living standards. Since World War II, the impressive growth of the manufacturing, mining, and service sectors has transformed the nation from a largely rural economy into one primarily industrial and urban. Real rates of growth have averaged nearly 3.0% since 1993. Unemployment is falling and government budget surpluses are being partially devoted to reducing the large public sector debt. The 1989 US-Canada Free Trade Agreement (FTA) and 1994 North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) (which included Mexico) have touched off a dramatic increase in trade and economic integration with the US. With its great natural resources, skilled labor force, and modern capital plant Canada can anticipate solid economic prospects in the future. The continuing constitutional impasse between English- and French-speaking areas is raising the possibility of a split in the federation, making foreign investors somewhat edgy. GDP: purchasing power parity—$688.3 billion (1998 est.) GDP—real growth rate: 3% (1998 est.) GDP—per capita: purchasing power parity—$22,400 (1998 est.)
GDP—composition by sector:
Population below poverty line: NA%
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
Inflation rate (consumer prices): 0.9% (1998) Labor force: 15.8 million (1998) Labor force—by occupation: services 75%, manufacturing 16%, construction 5%, agriculture 3%, other 1% (1997) Unemployment rate: 7.8% (December 1998)
Budget:
Industries: processed and unprocessed minerals, food products, wood and paper products, transportation equipment, chemicals, fish products, petroleum and natural gas Industrial production growth rate: 0.8% (1998 est.) Electricity—production: 549.162 billion kWh (1996)
Electricity—production by source:
Electricity—consumption: 511.586 billion kWh (1996) Electricity—exports: 45.28 billion kWh (1996) Electricity—imports: 7.705 billion kWh (1996) Agriculture—products: wheat, barley, oilseed, tobacco, fruits, vegetables; dairy products; forest products; fish Exports: $210.7 billion (f.o.b., 1998) Exports—commodities: motor vehicles and parts, newsprint, wood pulp, timber, crude petroleum, machinery, natural gas, aluminum, telecommunications equipment Exports—partners: US 81%, Japan 4%, UK, Germany, South Korea, Netherlands, China (1997) Imports: $202.7 billion (f.o.b., 1998) Imports—commodities: machinery and equipment, crude oil, chemicals, motor vehicles and parts, durable consumer goods Imports—partners: US 76%, Japan 3%, UK, Germany, France, Mexico, Taiwan, South Korea (1997) Debt—external: $253 billion (1996) Economic aid—donor: ODA, $2.1 billion (1995) Currency: 1 Canadian dollar (Can$) = 100 cents Exchange rates: Canadian dollars (Can$) per US$1—1.5192 (January 1999), 1.4835 (1998), 1.3846 (1997), 1.3635 (1996), 1.3724 (1995), 1.3656 (1994) Fiscal year: 1 April—31 March Telephones: 15.3 million (1990)
Telephone system:
excellent service provided by modern technology
Radio broadcast stations: AM 334, FM 35, shortwave 7 (one of the shortwave stations, Radio Canada International, has six transmitters, 48 frequencies, and broadcasts in seven languages; the transmissions are relayed by repeaters in Europe and Asia) (1998) Radios: NA Television broadcast stations: 80 (in addition, there are many repeaters) (1997) Televisions: 11.53 million (1983 est.)
Railways:
Highways:
Waterways: 3,000 km, including Saint Lawrence Seaway Pipelines: crude and refined oil 23,564 km; natural gas 74,980 km Ports and harbors: Becancour (Quebec), Churchill, Halifax, Hamilton, Montreal, New Westminster, Prince Rupert, Quebec, Saint John (New Brunswick), St. John's (Newfoundland), Sept Isles, Sydney, Trois-Rivieres, Thunder Bay, Toronto, Vancouver, Windsor
Merchant marine:
Airports: 1,395 (1998 est.)
Airports—with paved runways:
Airports—with unpaved runways:
Heliports: 16 (1998 est.) Military branches: Canadian Armed Forces (includes Land Forces Command or LC, Maritime Command or MC, Air Command or AC, Communications Command or CC, Training Command or TC), Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP) Military manpower—military age: 17 years of age
Military manpower—availability:
Military manpower—fit for military service:
Military manpower—reaching military age annually:
Military expenditures—dollar figure: $7.1 billion (FY97/98) Military expenditures—percent of GDP: 1.2% (FY97/98) Disputes—international: maritime boundary disputes with the US (Dixon Entrance, Beaufort Sea, Strait of Juan de Fuca, Machias Seal Island) Illicit drugs: illicit producer of cannabis for the domestic drug market; use of hydroponics technology permits growers to plant large quantities of high-quality marijuana indoors; growing role as a transit point for heroin and cocaine entering the US market

|
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
 |
|||||


