 |
|
General Information about India
Location: Southern Asia, bordering the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal, between Burma and Pakistan 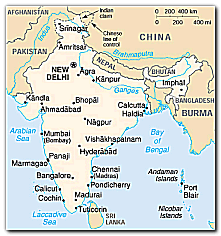
Geographic coordinates: 20 00 N, 77 00 E Map references: Asia
Area:
Area—comparative: slightly more than one-third the size of the US
Land boundaries:
Coastline: 7,000 km
Maritime claims:
Climate: varies from tropical monsoon in south to temperate in north Terrain: upland plain (Deccan Plateau) in south, flat to rolling plain along the Ganges, deserts in west, Himalayas in north
Elevation extremes:
Natural resources: coal (fourth-largest reserves in the world), iron ore, manganese, mica, bauxite, titanium ore, chromite, natural gas, diamonds, petroleum, limestone
Land use:
Irrigated land: 480,000 sq km (1993 est.) Natural hazards: droughts, flash floods, severe thunderstorms common; earthquakes Environment—current issues: deforestation; soil erosion; overgrazing; desertification; air pollution from industrial effluents and vehicle emissions; water pollution from raw sewage and runoff of agricultural pesticides; tap water is not potable throughout the country; huge and rapidly growing population is overstraining natural resources
Environment—international agreements:
Geography—note: dominates South Asian subcontinent; near important Indian Ocean trade routes Population: 1,000,848,550 (July 1999 est.)
Age structure:
Population growth rate: 1.68% (1999 est.) Birth rate: 25.39 births/1,000 population (1999 est.) Death rate: 8.5 deaths/1,000 population (1999 est.) Net migration rate: -0.08 migrant(s)/1,000 population (1999 est.)
Sex ratio:
Infant mortality rate: 60.81 deaths/1,000 live births (1999 est.)
Life expectancy at birth:
Total fertility rate: 3.18 children born/woman (1999 est.)
Nationality:
Ethnic groups: Indo-Aryan 72%, Dravidian 25%, Mongoloid and other 3% Religions: Hindu 80%, Muslim 14%, Christian 2.4%, Sikh 2%, Buddhist 0.7%, Jains 0.5%, other 0.4%
Languages:
English enjoys associate status but is the most important language for
national, political, and commercial communication, Hindi the national
language and primary tongue of 30% of the people, Bengali (official),
Telugu (official), Marathi (official), Tamil (official), Urdu (official),
Gujarati (official), Malayalam (official), Kannada (official), Oriya
(official), Punjabi (official), Assamese (official), Kashmiri (official),
Sindhi (official), Sanskrit (official), Hindustani (a popular variant of
Hindi/Urdu spoken widely throughout northern India)
Literacy:
Country name:
Data code: IN Government type: federal republic Capital: New Delhi Administrative divisions: 28 states and 7 union territories*; Andaman and Nicobar Islands*, Andhra Pradesh , Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Bihar, Chandigarh*, Chattisgarh, Dadra and Nagar Hav eli*, Daman and Diu*, Delhi*, Goa, Gujarat, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Jharkhand, Karnataka, Kerala, Lakshadweep*, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtr a, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Orissa, Pondicherry*, Punjab, Rajastha n, Sikkim, Tamil Nadu, Tripura, Uttaranchal, Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal Independence: 15 August 1947 (from UK) National holiday: Anniversary of the Proclamation of the Republic, 26 January (1950) Constitution: 26 January 1950 Legal system: based on English common law; limited judicial review of legislative acts; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction, with reservations Suffrage: 18 years of age; universal
Executive branch:
Legislative branch:
bicameral Parliament or Sansad consists of the Council of States or Rajya
Sabha (a body consisting of not more than 250 members, up to 12 of which
are appointed by the president, the remainder are chosen by the elected
members of the state and territorial assemblies; members serve six-year
terms) and the People's Assembly or Lok Sabha (545 seats; 543 elected by
popular vote, 2 appointed by the president; members serve five-year terms)
Judicial branch: Supreme Court, judges are appointed by the president and remain in office until they reach the age of 65 Political parties and leaders: Bharatiya Janata Party or BJP [Kushabhau THAKRE, president, L. K. ADVANI, A. B. VAJPAYEE]; Congress (I) Party [Sonia GANDHI, president]; Janata Dal Party [Sharad YADAV, president, I. K. GUJRAL]; Janata Dal (Ajit) [Ajit SINGH]; Rashtriya Janata Dal or RJD [Laloo Prasad YADAV]; Communist Party of India/Marxist or CPI/M [Harkishan Singh SURJEET]; Tamil Maanila Congress [G. K. MOOPANAR]; Dravida Munnetra Kazagham or DMK (a regional party in Tamil Nadu) [M. KARUNANIDHI]; Samajwadi Party or SP [Mulayam Singh YADAV (president), Om Prakash CHAUTALA, Devi LAL]; Telugu Desam (a regional party in Andhra Pradesh) [Chandrababu NAIDU]; Communist Party of India or CPI [Indrajit GUPTA]; Revolutionary Socialist Party or RSP [Tridip CHOWDHURY]; Asom Gana Parishad [Prafulla Kumar MAHANTA]; Congress (Tiwari) [Arjun SINGH and N. D. TIWARI]; All India Forward Bloc or AIFB [Prem Dutta PALIWAL (chairman), Chitta BASU (general secretary)]; Muslim League [G. M. BANATWALA]; Madhya Pradesh Vikas Congress [Madhavro SCINDIA]; Karnataka Congress Party [S. BANGARAPPA]; Shiv Sena or SHS [Bal THACKERAY]; Bahujan Samaj Party or BSP [Kanshi RAM]; Communist Party of India/Marxist-Leninist or CPI/ML [Vinod MISHRA]; Akali Dal factions representing Sikh religious community in the Punjab; National Conference or NC (a regional party in Jammu and Kashmir) [Farooq ABDULLAH]; Bihar Peoples Party [Lovely ANAND]; Samata Party or SAP (formerly Janata Dal members) [George FERNANDES]; Indian National League [Suliaman SAIT]; Kerala Congress (Mani faction) [K. M. MANI]; All India Anna Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam or ADMK [leader NA]; Biju Janata Dal or BJD [leader NA]; Trinamool Congress [leader NA] Political pressure groups and leaders: various separatist groups seeking greater communal and/or regional autonomy; numerous religious or militant/chauvinistic organizations, including Adam Sena, Ananda Marg, Vishwa Hindu Parishad, and Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh International organization participation: AfDB, AsDB, BIS, C, CCC, CP, ESCAP, FAO, G- 6, G-15, G-19, G-24, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICFTU, ICRM, IDA, IEA (observer), IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Inmarsat, Intelsat, Interpol, IOC, IOM (observer), ISO, ITU, MIPONUH, MONUA, NAM, OAS (observer), OPCW, PCA, SAARC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIKOM, UNITAR, UNMIBH, UNOMIL, UNOMSIL, UNU, UPU, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WToO, WTrO
Diplomatic representation in the US:
Diplomatic representation from the US:
Economy—overview: India's economy encompasses traditional village farming, modern agriculture, handicrafts, a wide range of modern industries, and a multitude of support services. 67% of India's labor force work in agriculture, which contributes 25% of the country's GDP. Production, trade, and investment reforms since 1991 have provided new opportunities for Indian businesspersons and an estimated 300 million middle class consumers. New Delhi has avoided debt rescheduling, attracted foreign investment, and revived confidence in India's economic prospects since 1991. Many of the country's fundamentals—including savings rates (26% of GDP) and reserves (now about $30 billion)—are healthy. Even so, the Indian Government needs to restore the early momentum of reform, especially by continuing reductions in the extensive remaining government regulations. India's exports, currency, and foreign institutional investment were affected by the East Asian crisis in late 1997 and 1998; but capital account controls, a low ratio of short-term debt to reserves, and enhanced supervision of the financial sector helped insulate it from near term balance-of-payments problems. Exports fell 5% in 1998 mainly because of the fall in Asian currencies relative to the rupee. Energy, telecommunications, and transportation bottlenecks continue to constrain growth. A series of weak coalition governments have lacked the political strength to push reforms forward to address these and other problems. Indian think tanks project GDP growth of about 4.5% in 1999. Inflation will remain a worrisome problem. GDP: purchasing power parity—$1.689 trillion (1998 est.) GDP—real growth rate: 5.4% (1998 est.) GDP—per capita: purchasing power parity—$1,720 (1998 est.)
GDP—composition by sector:
Population below poverty line: 35% (1994 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
Inflation rate (consumer prices): 14% (1998 est.) Labor force: NA Labor force—by occupation: agriculture 67%, services 18%, industry 15% (1995 est.) Unemployment rate: NA%
Budget:
Industries: textiles, chemicals, food processing, steel, transportation equipment, cement, mining, petroleum, machinery Industrial production growth rate: 5.5% (1997) Electricity—production: 404.475 billion kWh (1996)
Electricity—production by source:
Electricity—consumption: 406.02 billion kWh (1996) Electricity—exports: 130 million kWh (1996) Electricity—imports: 1.675 billion kWh (1996) Agriculture—products: rice, wheat, oilseed, cotton, jute, tea, sugarcane, potatoes; cattle, water buffalo, sheep, goats, poultry; fish Exports: $32.17 billion (f.o.b., 1998) Exports—commodities: textile goods, gems and jewelry, engineering goods, chemicals, leather manufactures Exports—partners: US 19%, Hong Kong 6%, UK 6%, Japan 6%, Germany 5% (1997) Imports: $41.34 billion (c.i.f., 1998) Imports—commodities: crude oil and petroleum products, machinery, gems, fertilizer, chemicals Imports—partners: US 10%, Belgium 7%, UK 7%, Germany 7%, Saudi Arabia 6%, Japan 6% (1997) Debt—external: $93 billion (1998) Economic aid—recipient: $1.604 billion (1995) Currency: 1 Indian rupee (Re) = 100 paise Exchange rates: Indian rupees (Rs) per US$1—42.508 (January 1999), 41.259 (1998), 36.313 (1997), 35.433 (1996), 32.427 (1995), 31.374 (1994) Fiscal year: 1 April—31 March Telephones: 12 million (1996)
Telephone system:
mediocre; local and long distance service provided throughout all regions
of the country, with services primarily concentrated in the urban areas;
major objective is to continue to expand and modernize long-distance
network in order to keep pace with rapidly growing number of local
subscriber lines; steady improvement is taking place with the recent
admission of private and private-public investors, but demand for
communication services is also growing rapidly
Radio broadcast stations: AM 153, FM 91, shortwave 62 (1998 est.) Radios: 111 million (1998 est.) Television broadcast stations: 562 (82 stations have 1 kW or greater power and 480 stations have less than 1 kW of power) (1997) Televisions: 50 million (1999 est.)
Railways:
Highways:
Waterways: 16,180 km; 3,631 km navigable by large vessels Pipelines: crude oil 3,005 km; petroleum products 2,687 km; natural gas 1,700 km (1995) Ports and harbors: Calcutta, Chennai (Madras), Cochin, Jawaharal Nehru, Kandla, Mumbai (Bombay), Vishakhapatnam
Merchant marine:
Airports: 341 (1998 est.)
Airports—with paved runways:
Airports—with unpaved runways:
Heliports: 17 (1998 est.) Military branches: Army, Navy (including naval air arm), Air Force, various security or paramilitary forces (includes Border Security Force, Assam Rifles, and Rashtriya Rifles) Military manpower—military age: 17 years of age
Military manpower—availability:
Military manpower—fit for military service:
Military manpower—reaching military age annually:
Military expenditures—dollar figure: $10.012 billion (FY98/99) Military expenditures—percent of GDP: 2.7% (FY98/99) Disputes—international: boundary with China in dispute; status of Kashmir with Pakistan; water-sharing problems with Pakistan over the Indus River (Wular Barrage); a portion of the boundary with Bangladesh is indefinite; dispute with Bangladesh over New Moore/South Talpatty Island Illicit drugs: world's largest producer of licit opium for the pharmaceutical trade, but an undetermined quantity of opium is diverted to illicit international drug markets; major transit country for illicit narcotics produced in neighboring countries; illicit producer of hashish and methaqualone; cultivated 2,050 hectares of illicit opium in 1997, a 34% decrease from 1996, with a potential production of 30 metric tons, a 36% decrease from 1996

|
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
 |
|||||


